Pavement ants are hardy creatures, able to thrive beneath cracks, sidewalks, stone, concrete slabs, and more.
To get rid of pavement ants, you can use ant baits, which is an environmentally friendly form of chemical control. Additionally, insecticides in the form of powder or dust can also help eradicate pavement ant colonies, although it may take longer to see results.
Of course, the best course of action is to prevent an infestation from occurring in the first place. Keeping your surroundings clean, regularly disposing of garbage and leftovers, and ensuring that there are no cracks or holes in your home that could provide shelter for pavement ants are all effective preventative measures.
What Are Pavement Ants?
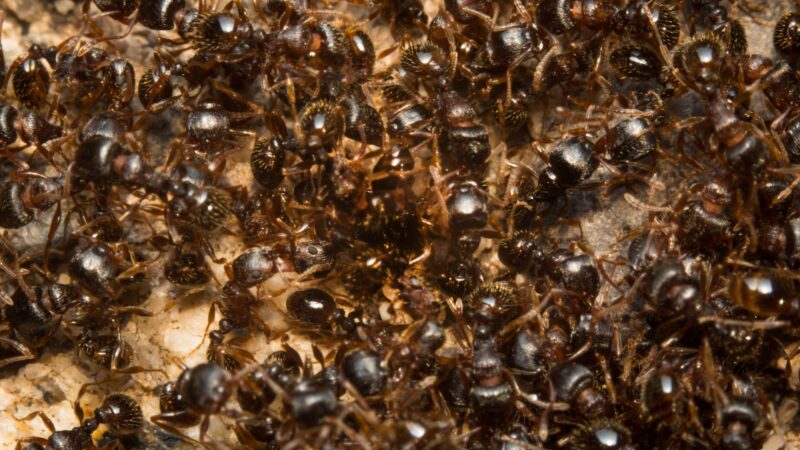

Pavement ant (Tetramorium caespitum) is one of the most commonly found pests and some people also call them sugar ants due to their fondness for sweet foods. Pavement ants are believed to have originated in Europe but are now found in various regions worldwide, including the United States.
The name pavement ant is given to them because they make their shelter underneath pavements. You will find pavement and mounds under floors, under concrete slabs and bricks, landscaping, in driveways, in walls, near water heaters, on the trash, in insulations, etc.
How Do They Look Like?
Pavement Ants have dark brown to blackish appearance, they are about 2.5 to 3 mm long. Their body consists of different segments, head, thorax, and legs. The head and thorax are darker and have parallel markings whereas the legs and antennae are lighter in color. The antennae on the head have 12 segments.
How Long Do They Live?
The pavement ants have a caste system that consists of workers, reproductive males, and winged females (queens). The workers take care of the colony and find food. Each colony has one or more than one queen.
The pavement ants mate during spring and summer. After mating, the queen lays eggs, males die and mated females shed their wings and move to a different place to start a new colony. The eggs develop into adults (workers) in 40-60 days. The workers can live up to 5 years but males used for reproducing die after a few months.
What Do They Eat?
Pavement ants feed upon leftovers, dead matter (scavengers), honeydew, sugary and greasy foods, pet food, meat, grasses, seeds, insects, etc. They know the path back to their nest after the food collection and travel back in lines by maintaining discipline. When moving back to the nest, they release the scent through a stinger (at the tip of the abdomen) which helps the workers to find the food source.
Related: What Do Ants Eat? | Ant Feeding Habits
Can They Damage House?
Pavement ants do not cause any structural damage to houses. However, large colonies of pavement ants can be very annoying and disgusting. These ants can attack your food and spoil it. The pavement ants can carry bacteria or viruses from the garbage or leftovers into your house. To avoid potential damage, you can apply different methods to eradicate them.
Is Their Bite Dangerous?
Pavement ants and their venom are not a danger to humans. They are docile in nature and are more interested in finding food for their colonies. Although pavement ants are typically docile, they can sting if they feel threatened. Pavement ant sting can be mildly painful and cause itching. Also, in some cases even allergic reactions.
How to Get Rid of Pavement Ants: Instructions

The first step is the inspection of pavement ants in your house or outdoors. Once you confirm their identity, you can apply the following methods to eliminate them.
Method 1: Ant Baiting
One of the best ways to get rid of pavement ants infestation is using ant baits. Slow-acting baits may take time to show the results but they are very efficient. There are different types of baits available in the market such as sugar baits, fat-based baits, or protein-based baits.
Dust and insecticide sprays will scatter and quickly kill the worker ants and they will not get the chance to return to their nest. If the queen stays alive the colony will survive and eventually grow again in numbers.
When you use ant baits and successfully lure the ants, they will take the bait to their shelters and if the queen and workers feed upon it, it will result in the eradication of the entire colony.
You can also change the bait if the current bait does not show good results.
No products found.
Method 2: Insecticide Spray
Different indoor and outdoor insecticide sprays are used to control pavement ants. These sprays come with instructions and labels. You can follow the company guidelines for effective results. Apply the spray on all the cracks, crevices, holes, and mounds.
The following are the most recommended sprays for pavement ants and most ants in general.
No products found.
Keep the pets and children away for 2 to 4 hours for safety purposes.
Method 3: Dust Treatment
The dust treatment can be helpful to eliminate the pavement ant colonies. Apply the dust at the entry points, holes, and cracks of your house by following the instruction manual provided with the insecticides.
How to Get Rid of Pavement Ants Naturally | Natural Methods
Diatomaceous Earth
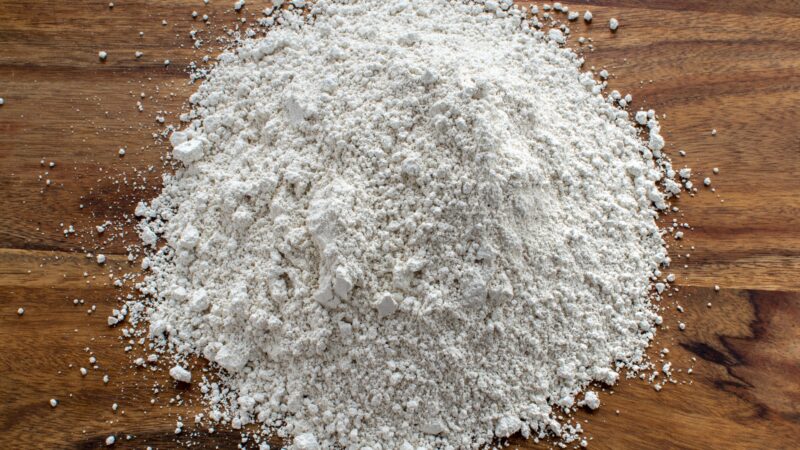

The Diatomaceous Earth powder is an eco-friendly, organic, and harmless method to keep the pavement ants away from your house. You can sprinkle the powder at the different entry points and cracks inside the house to protect your house from these pests.
Boiling Water
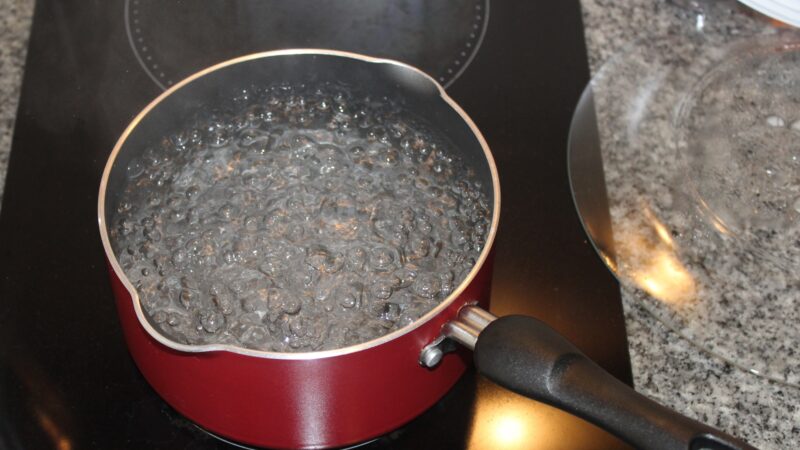

One of the commonly used natural methods to get rid of ants is by pouring hot water into the shelters of pavement ants. This method is very effective in eliminating ant infestations, but should only be used outside, as pouring hot water indoors can cause damage.
Natural Baits
To prepare natural ant bait, mix 2 tablespoons of honey, 2 tablespoons of peanut butter, and a half teaspoon of borax. Place it near the entry point or cupboards to lure the pavement ants. Replace the bait after it gets dry. You can also mix sugar and borax or honey and borax to make different ant baits.
Herbs and Spices

Use ant-repellent spices and herbs to keep the pavement ants away from the house. Place the insect repellent herbs at the entry point of pavement ants to prevent their colonization. Some of the ant-repellent herbs and spices are whole cloves, bay leaves, cinnamon, turmeric, cayenne pepper, citrus oil, lavender oil, etc. Keep replacing the herbs or spices when they lose their scent.
Water and Vinegar
To make a natural vinegar-based pesticide, mix apple cider vinegar and water in an equal ratio (1:1). Apply the vinegar spray at the entry points and shelters of pavement ants.
Soapy Water
Prepare the soap and water solution for the excellent homemade insecticide spray. Take 1 cup of water and add around half a cup of dishwashing soap in it. Mix it thoroughly and pour the mixture into the spray bottle. Spray this mixture directly on the ants and their nests to eliminate them.
Ground Coffee

Place the ground coffee near cracks and holes in the house. The ground coffee will act as a repellent for the pavement ants and will prevent them from colonization.
How to Get Rid of Pavement Ants in Walls?
Seal all the cracks in the walls to prevent the colonization of pavement ants in those places. You can use natural or synthetic sprays to eradicate pavement ant infestation in the walls. Natural repellents, herbs, or spices are other effective ways to keep them away.
Pavement vs Carpenter Ants: Differences
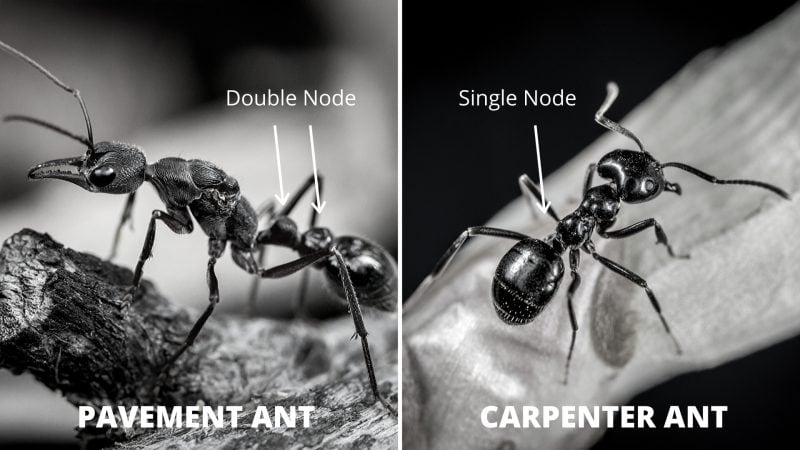
Pavement ants are smaller than carpenter ants, typically measuring 2.5 to 4 millimeters in length, while carpenter ants can measure 3.5 to 13 millimeters Carpenter ants are destructive in nature, damage wood, and can cause structural losses while pavement ants are harmless in nature. The pavement ants are brown to black in color, whereas carpenter ants have a variety of colors such as yellow, orange, red, and brown-black. They look almost the same but there is a difference in the number of nodes as is seen in the picture. Carpenter ants have one while pavement ants have two.
Prevent Pavement Ant From Invading Your House
The final step is the prevention of the pavement and re-infestation. You can take the following preventive measure to stop the infestation of pavement ants from happening again.
- Seal all possible entry points for pavement ants in your house, including holes, cracks, and crevices. The ants get attracted to the wet, warm, and dirty areas where they find food sources.
- Good sanitation practices are the critical step to preventing pavement ant infestations. Take care of cleanliness and sweep your kitchen counters after every meal. Fix any water leakage problems in your house.
- Remove all the construction materials, bricks, or concrete slabs piled up around your house to remove places where pavement ants set up their shelters.
- Prune all the grasses, bushes, creeper, or crawler plants in your lawn that can act as a bridge entry for the pavement ants.
List of Sources
Pavement ant – Tetramorium caespitum, University of Florida
Pavement Ant, The Pennsylvania State University
Potter M., Ant Control for Householders, University of Kentucky College of Agriculture
Hoover, K. M., Bubak, A. N., Law, I. J., Yaeger, J., Renner, K. J., Swallow, J. G., & Greene, M. J. (2016). The organization of societal conflicts by pavement ants Tetramorium caespitum: an agent-based model of amine-mediated decision making
von Sicard N.A., Candy D.J., Anderson M., The biochemical composition of venom from the pavement ant (Tetramorium caespitum L.), School of Biological Sciences, University of Birmingham, U.K.
- How to Get Rid of Copperheads | Practical Guide - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Corn Snakes | What Makes Them Aggressive? - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Alligators | Safety Measures and Removal Methods - July 16, 2023
