Bed bugs and scabies mites are parasites since both of them feed on human blood. Despite being different organisms, some people mistake one for the other.
What’s the difference between bed bugs and scabies? The most important difference between them is that bed bugs don’t live in humans, while scabies burrow into the skin to live and lay eggs. Bed bugs don’t carry diseases, but scabies mites do. Lastly, bed bugs can be seen by the naked eye, while scabies mites are microscopic.
Bed bugs and scabies mites are common pests in households. Both of them may suck animal blood, but some of their species prefer feeding on human blood.
Treatments for bed bug bites also differ from treating scabies. In this complete guide, you will learn everything you should know about bed bugs and scabies.
Bed bug Identification
What Are Bed Bugs?
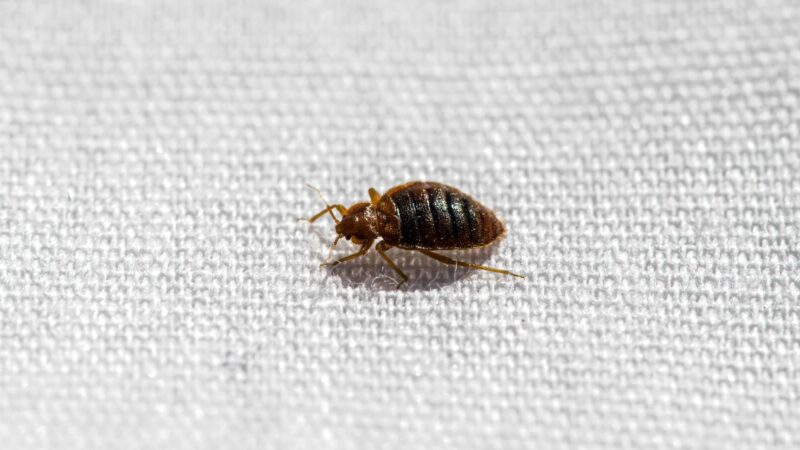

Bed bugs are tiny insects in the order of Hemiptera that suck blood to survive and reproduce. Some bed bug species suck the blood of warm-blooded animals, but two major species prefer feeding on human blood.
They are the cosmopolitan bed bugs (Cimex lectularius and the tropical bed bugs (Cimex hemipterus).
Related: What Are Bed Bugs? (Origins, History, Evolution & More)
How to Identify Bed Bugs?
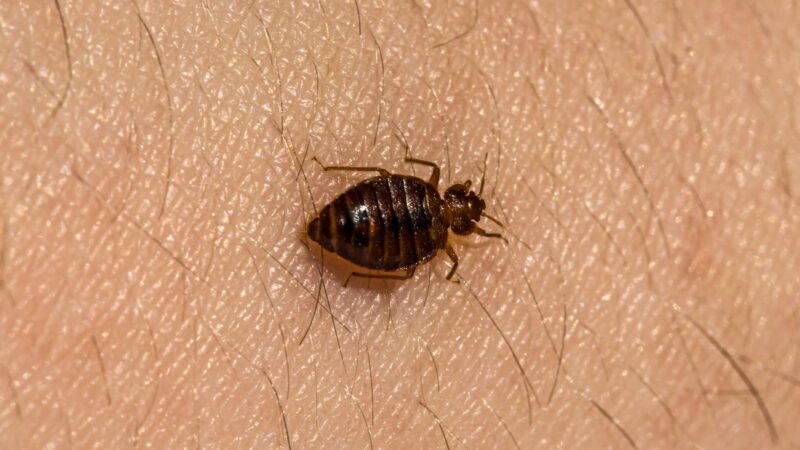

Adult bed bugs are about 1/4 inches (6.35 mm.) in length, with oval, flat bodies that are mahogany to a rusty brown when unfed. After feeding, their body will turn dark red and become bigger.
They have sucking mouthparts, four-segment antennae, and six slender legs. Nymphs look like adults, except they are smaller.
Adult and baby bed bugs have narrow heads and a pair of black eyes. Their bodies are covered with short, golden hairs. Bed bugs also have a wing pad but no wings, which means that they cannot fly.
Their legs are not designed for jumping, but they crawl fast. They produce a smelly odor through their glands.
How Long Do Bed Bugs Live?
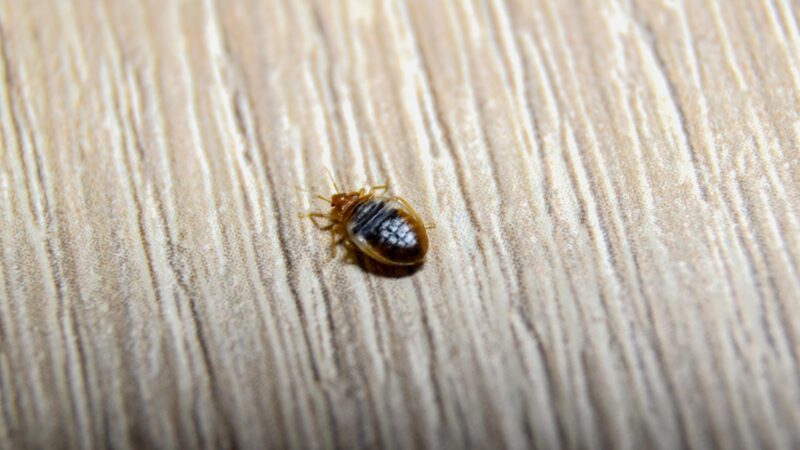

Depending on the temperature and availability of food, adult bed bugs can live for a year or more. At low temperatures, they can survive up to 400 days without a blood meal.
Nonetheless, these adults cannot lay eggs without feeding. Older nymphs can survive longer without food, as compared to younger ones.
How Do You Get Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs can sense human body heat, which is why they usually live close to humans. These notorious bloodsuckers usually hide in tiny dark cracks and crevices in beds, chairs, and other furniture where people stay for a long time. Most bed bugs prefer attacking humans at night while they are sleeping.
Related: Bed Bug Preferences: What Attracts Bed Bugs?
Can Bed Bugs Spread Diseases?
Bed bugs don’t spread infectious diseases. However, they bite humans and inject a natural anesthetic into the skin while feeding. This is why bed bug bites are usually felt only hours after the attack.
Most bed bug bites are very itchy and can cause skin swelling, but some people don’t show any symptoms at all.
Related: Bed Bug Bites: How to Treat Bed Bug Bites and Prevent Them
How Do I Get Rid of Bed Bugs in My Bed?
Eliminating bed bugs can be very challenging because they seem to be coming out of nowhere. Some skin swelling and itchiness are not caused by bed bug bites. This is why you have to investigate further.
But if you see bed bugs in your bed, here are some useful tips to get rid of them once and for all:
1. Wash all the bedding with hot water.
Remove the blankets, bed sheets, mattress covers, linens, and other washable fabrics from your bed. Wash them with hot water and detergent. Dry them with a hot dryer.
Bed bug eggs, nymphs, and adults die if they are exposed to 45°C (113°F) for about 30 minutes. Make sure your fabrics can withstand the heat.
2. Steam clean your mattress.
Vacuum the surface and corners of your mattress, especially if they have bloodstains, which are bed bug feces. These are human blood that bed bugs have ingested and expelled.
To make sure all bed bugs are killed, clean your mattress with a steam cleaner such as .
No products found.
3. Inspect your bed thoroughly.
Inspect your bed thoroughly with a flashlight and an old credit card. If possible, dismantle your bed and carefully check the bed frame, joints, box spring, and headboard.
Move the card along the tiny spaces of your bed. Here, you may also find some bed bug eggs, which are oval and white and are usually in clusters.
4. Kill bed bugs in your bed.
To capture and kill bed bugs in your bed, you may use packing tape as you see them. You may also kill them using a piece of cloth with hot water and detergent.
Alternatively, apply or spray pyrethrin insecticide such as . Just make sure you follow the directions correctly.
No products found.
Related: Natural Ways to Get Rid of Bed Bugs: A Complete Guide
Scabies Identification
What Are Scabies Mites?
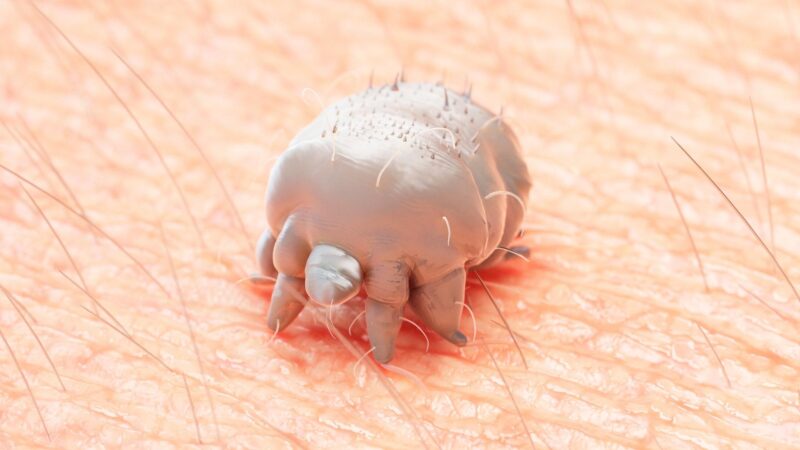
Scientifically known as Sarcoptes scabiei, scabies mites are not insects but rather tiny arachnids and are relatives of ticks and spiders. They use humans as their primary hosts.
These cosmopolitan parasites are commonly found in crowded places such as prisons, nursery homes, and extended-care facilities.
How to Identify Scabies Mites?
Also called human itch mites, adult scabies mites have oval, flattened, whitish-brown bodies and eight cylindrical legs. Their bodies are covered with long hair. They have no eyes, and are, therefore, blind.
Female scabies mites are 0.30-0.45 mm long and 0.25-0.35 mm wide; while males are only about half their sizes.
Scabies larvae and nymphs look like adults, except that they are much smaller. Larvae have six legs and are slightly smaller than nymphs.
On the other hand, nymphs have eight legs and undergo two nymphal stages before they become adults. The life cycle of scabies mites is completed within 10-17 days.
Related: 8 Tiny Bugs in Bed but Not Bed Bugs | How to Identify and Eliminate Them!
How Long Do Scabies Mites Live?
While hosting on humans, adult female scabies mites can have a lifespan of between 1 to 2 months. But when unattached to their host, they will die in 10 minutes if the temperature is 49°C (120°F).
Nevertheless, scabies mites may still survive for 2-3 days without a host if the temperature is around 25°C (77°F).
How Do You Get Scabies?
You can get scabies through prolonged or frequent skin-to-skin contact with a person that already has scabies mites. This contagious skin infection can also be transmitted through shared towels, clothing, and bedding. Scabies mites burrow into the outer layer of skin of their host and lay eggs there for the rest of their lives.
Can Scabies Spread Diseases?
Scabies can spread diseases via direct and indirect contact with an infected person. This includes sex and sharing infested items. Symptoms include skin rashes and extreme itchiness.
Elderly people who have crusted scabies (Norwegian) can spread the disease through a quick hug or handshake.
How Do I Get Rid of Scabies Mites on My Bed?
Scabies mites usually attack thin skin, including hands and feet, especially between the fingers and toes, around the armpit, breast, buttocks, and genitals.
If a family member has been diagnosed with scabies, actions should be taken as soon as possible. Here are some effective ways to get rid of scabies mites on your bed:
1. Wash bedding with hot water.
If the infected person shares the bed with you, wash the bed sheet, blanket, and linens with hot water and detergent. Scabies mites die if you expose them to temperatures of 50°C (122°F) and above for 10 minutes.
For infested but non-washable items, place them inside in a plastic bag and leave them for 3 days.
2. Wash the clothes of an infected person with hot water.
Aside from bedding, scabies can also spread through the clothes and towels of the infected person. Regardless of whether he shares them with you or not, you should also wash them at the same temperature.
To make sure that scabies mites are killed, use a hot dryer when drying them. Don’t use them for at least 72 hours.
Bed Bugs vs. Scabies: Similarities and Differences
Both bed bugs and scabies mites feed on human blood. Bed bugs don’t transmit diseases, while scabies mites cause scabies. You can also see bed bugs, but you need a magnifying glass to see scabies.
With that, here is a summary of the similarities and differences between them:
- Bed bugs are insects, while scabies mites are arachnids.
- Nymph bed bugs and scabies look like their adults but are much smaller.
- Both bed bugs and scabies don’t undergo the pupal stage.
- Scabies mites have larvae, which have six legs. Bed bugs have no larvae.
- Both of them don’t have wings; they cannot fly or jump.
- Bed bugs can see humans, while scabies mites are blind,
- Scabies mites lay eggs on humans, while bed bugs lay eggs on cracks and crevices.
- Without food or a host, bed bugs can survive longer than scabies mites.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You See Scabies Mites?
You cannot see scabies mites with the naked eye since they are very tiny. In fact, you can only see them if you use a magnifying glass or you place them under a microscope.
But for heavily infected individuals, adult scabies mites may look like tiny black spots on the skin. On the other hand, nymphs are invisible.
How Do I Know if I Have Scabies?
Unfortunately, it is quite difficult to know right away if you have scabies. A person who is infected for the first time may feel the symptoms within 4-6 weeks.
People who previously had scabies may show symptoms only after a few days. Elderly people or those with a weak immune system are more prone to scabies.
Scabies Treatment
First of all, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasized that there is no “over-the-counter” medicine that is approved as a treatment for scabies.
Any medication should be taken with a doctor’s prescription. Meanwhile, here are some possible recommendations that may come from your doctor:
1. Elimite Permethrin Cream
Elimite Permethrin Cream (5% permethrin) is generally safe and effective in killing scabies and eggs. This cream is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a treatment for scabies in people aged 2 months and above. Never use applications more than what is prescribed by your doctor.
2. Crotamiton Lotion or Cream
Crotamiton lotion or cream (10% Crotamiton) is also safe and effective in killing scabies and eggs. Among the popular brands are Eurax and Crotan. Both of them are FDA-approved as scabies treatment but for adults only and not for children. Nonetheless, this medication is sometimes not effective for adults.
3. Sulfur Ointment
Sulfur ointment (5%-10% sulfur) is not FDA-approved but considered safe for treating scabies in infants less than 2 months of age. Based on a study, it is more effective when applied for 3 consecutive days. However, sulfur has some side effects, such as a mild burning sensation and leaves an unpleasant odor.
4. Lindane Lotion
Lindane lotion (1% lindane) is FDA-approved for treating scabies in adults but is not recommended as a first-line treatment. Formerly known as gamma benzene hexachloride, lindane should not be used in premature infants, people less than 110 pounds or experiencing seizures, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers.
What Is the Main Cause of Bed Bugs?
The main cause of bed bugs is when people travel domestically or internationally without knowing that they have bed bugs. These bloodsucking creatures love to hitchhike in bags, suitcases, clothes, and other belongings. Bed bugs can be accidentally brought home when people sleep in hotels or other houses.
How Can I Tell if We Have Bed Bugs?
Waking up one morning feeling itchy on your skin with some swelling does not automatically mean that you have bed bugs. This is because some bed bug bites look like mosquito bites, or they can be due to an allergy to something else. Therefore, here are some solid proofs that can tell you that you have bed bugs at home:
- Bloodstains on your bedding. These are bed bug feces.
- Presence of bed bug cast skin. Bed bug nymphs molt 5 times before they become adults.
- There are bed bug eggs on cracks and joints in your bed.
- The distinct moldy odor produced by bed bugs.
- You see some bed bugs, dead or alive.
Bed Bug Bite Treatment
Most bed bug bites don’t pose serious health risks except for itchiness and burning skin sensation. Bed bugs usually bite on exposed skin, such as arms, hands, face, and neck.
In most cases, these bites heal within 1-2 weeks after treatment. If you are sure you have bed bug bites, here is how to treat them:
- To reduce itchiness and avoid skin infection, wash them with soap and water.
- Don’t scratch the infected area. For babies bitten by bed bugs, cut their nails short so they cannot scratch them.
- For additional relief, apply a cold compress (ice pack) to the infected skin.
- Apply antiseptic creams or ointments such as . For babies, consult a pediatrician before applying anything to them.
- If there is a skin infection, consult a doctor before taking antibiotics.
Homemade Remedies for Bed Bugs and Scabies
Controlling bed bugs and scabies can be expensive and very frustrating, especially if the infestations are already severe. To avoid that from happening, you should take action as early as possible. So, once you see some early signs of bed bugs and scabies, here are some homemade remedies that you can try:
Homemade Remedies for Bed Bugs
- Dip bedding and blankets in hot water at 45°C (113°F) for at least 30 minutes.
- For bed frames and mattresses, use a reliable steam cleaner.
- According to a study, some essential oils can repel bed bugs. This includes citronella essential oil, clove essential oil, and peppermint essential oil.
- Sprinkle diatomaceous earth (DE) on areas where bed bugs could be hiding. is safe for humans and pets but kills bed bugs on contact.
No products found.
Homemade Remedies for Scabies
- Essential oils from clove, lavender, neem, orange, peppermint, and tea tree can kill scabies. However, more research is required to prove their efficacy.
- Cayenne pepper contains capsaicin, which according to a study, treats chronic soft tissue pain. There is no scientific evidence about treating scabies, though.
- Heat treatment. As mentioned earlier, washing infested bedding, clothes, and towels with hot water kills scabies.
Note: Some people may experience allergic reactions to essential oils and cayenne pepper. Always conduct a patch test on your skin before using them.
What Sprays Work on Bed Bugs and Scabies?
Permethrin sprays such as kill bed bugs and scabies. Just make sure you spray them only on clothes and mattresses but not on the skin. Essential oils can also be used as sprays, but there is no guarantee that they will always work on both parasites.
No products found.
Related: Top 10 Bed Bug Sprays | Safest and Most Effective Options
List of Sources
Sutherland, A. M., Choe, D.-H., Lewis, V. R. (2013). Bed Bugs. Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of California.
Quesada, C., Gripp, G. (2020). Biology, Habitat, and Management of Bed Bugs. PennState Extension.
Bed Bugs Appearance and Life Cycle. United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Scabies Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). (2020). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Sharquie, K. E., et al. (2012). Treatment of scabies using 8% and 10% topical sulfur ointment in different regimens of application. J Drugs Dermatol.
- How to Get Rid of Copperheads | Practical Guide - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Corn Snakes | What Makes Them Aggressive? - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Alligators | Safety Measures and Removal Methods - July 16, 2023
