As you most likely know by now, bed bugs are notorious bloodsuckers and annoying house pests.
They are incredibly small, very good at hitchhiking and hiding in various places, and can also cause emotional distress. But what about baby bed bugs? Do they also bite humans?
Do baby bed bugs bite? Baby bed bugs bite humans just like adults do. A nymph must consume blood immediately as it hatches in order to survive, grow, and shift to the following stage. They will pierce their skin with their elongated mouthparts. The bites will also cause itchy, red bumps on the skin.
Scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, bed bugs are commonly found in many places, including homes, offices, schools, and even in public transport.
Also called nymphs, baby bed bugs may stay with adults but can also live alone. Below are some of the frequently asked questions about baby bed bugs:
What Do Baby Bed Bugs Look Like?
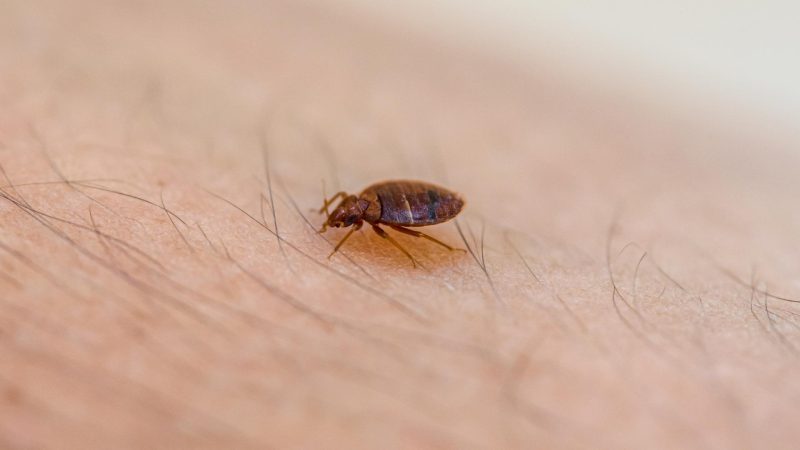

Baby bed bugs look like adults but are relatively smaller. Adults are about 1/5 inch long, while nymphs can be 1/20-1/5 inches long, depending on their age.
Like adults, they have compound eyes and flat, oval bodies but with a thinner outer skeleton. In short, young bed bugs are very difficult to see with the naked eye.
What Color Are Newborn Baby Bed Bugs?
Newborn bed bugs are yellow or colorless but they will turn dark red right after feeding. Shortly after the eggs are hatched, baby bed bugs will already start searching for blood.
At some point, these bed bug babies may also have a tiny red spot on their bodies, which is the remaining blood after their last meal.
How Small Are Baby Bed Bugs?
During the first nymphal stage, nymphs are about 1.5 mm and will grow at around 0.05 mm after each stage. Therefore, they will be about 4.5 mm on their 5th and final nymphal stage.
Their exact sizes vary and mainly depend on the amount of blood they feed. Bed bug nymphs molt before going to the next stage.
Related: Baby Bed Bugs | Nymphs: Facts, Size and How to Identify
Do Bed Bugs Have Larvae?
Bed bugs undergo simple metamorphosis, which means they don’t have larvae and pupal stages. In short, there’s no such thing as bed bug larvae and pupae.
Instead, baby bed bugs will emerge once their eggs are hatched. These microscopic bed bug nymphs grow slowly until they become full-grown adults.
How Long Before Baby Bed Bugs Become Adults?
Baby bed bugs undergo five developmental nymphal stages before they become adults.
This usually takes between 35 and 48 days, and they need to feed on blood at least once before going to the next stage. Nevertheless, development can be faster if temperatures are 70-82°F (21-27.7°C) and if food is sufficient.
What Do Bed Bug Eggs Look Like?
Bed bug eggs are about 1 mm and are as small as pinheads. They are usually hatched within 10-14 days on rough surfaces such as paper and wood near the sleeping area of humans.
In normal conditions, female bed bugs lay 2-5 white eggs per day. During their lifetime, they can lay between 200 and 500 eggs.
Do Baby Bed Bugs Crawl?
Baby bed bugs also crawl but slower than adults. They also have six legs but are not long enough to crawl very quickly.
Nymphs are so slow that you might think that they are not moving once you see them. They don’t crawl that often because they molt and shed their skin. Baby bed bugs don’t jump, though.
What Do Baby Bed Bug Bites Look Like?
Baby and adult bed bug bites have a similar appearance. The body’s allergic reaction is what causes the swelling/redness associated with a bed bug bite.
This happens as a result of the saliva the bed bug employs to numb the biting site. The body swells up to help with the removal of this because it perceives it as a substance that is unfamiliar.
The duration of a baby bed bug bite is the same as an adult’s. However, within two weeks, they will become pretty clear.
What Are the Symptoms of Baby Bed Bug Bites?
The following features can help you spot bed bug bites that are still in the early stages:
- Color. It is tiny, elevated, and has a darker red patch in the center.
- Sensation. The bites on your body may be from bed bugs if you see yourself rubbing at them since they are typically fairly itchy.
- Number of bites. Many other insects, such as spiders, often bite once or twice. A bedbug may itch repeatedly, each bite producing a line.
- Location. The face, neck, arms, and hands are common areas where bed bugs bite.
Are Baby Bed Bug Bites Dangerous?
Baby bed bugs bites are not dangerous. Just like adult bed bugs, nymphs don’t transmit diseases to people and pets.
In general, people don’t easily notice they have been bitten by bed bugs until they find an actual bug. This is because the bed bug bites are not painful right away, and the effect on the skin will be felt later.
When Do Baby Bed Bugs Bite?
Just like adults, baby bed bugs bite may bite humans whenever they are hungry. But since they are nocturnal creatures, they are mostly active at night and rest during the day.
Nymphs usually bite people who are sleeping but can still attack humans even if they are awake. After all, bed bug bites are not felt immediately.
Are Baby Bed Bug Bites Different From Adult Bites?
Baby bed bug bites look the same as bites from adults. Both of them may cause a red and slightly swollen mark and are itchy and irritating.
Bed bug bite marks can be in a straight line or random. Some people may develop serious skin problems and experience insomnia, while some may show bite marks only.
Related: Bed Bug Bites: How to Treat Bed Bug Bites and Prevent Them
Can Bed Bugs Harm a Newborn Baby?
Bed bugs can harm a newborn baby if given the opportunity. If your baby has just been born, baby bed bugs and adults can sense his or her presence and may launch an attack.
Generally speaking, bed bugs feed on any kind of living human being, as well as warm-blooded animals such as cats and dogs.
How Long Before a Baby Can Feel Bed Bug Bites?
At the early stage, bed bug bites on a baby and adults will not have any effect on the skin. This is due to the anesthetic that they inject during feeding.
Typically, it takes one day or more before bed bug bite marks appear on adults. But because babies are more sensitive than adults, they will feel the effect earlier.
How to Treat Bed Bug Bites?
You might attempt the following two methods if you’re looking for home treatments for bed bug bites:
- Cleanse the bites. Gently cleanse any bedbug bites you find with warm, soapy water.
- Put on a cream or lotion. Itching alleviation may be beneficial because scratching the bites might result in an infection.
Can Baby Bed Bugs Play Dead?

Baby bed bugs cannot play dead. Unlike lady beetles, robber flies, and rice weevils, bed bugs of all stages can’t pretend that they are dead.
If you find them dead, they are absolutely dead. There is no way that they are coming back to life. On the other hand, dying bed bugs may still try to move.
Related: What Does It Mean if You Find a Dead Bed Bug? | Important Facts!
What Do Dead Baby Bed Bugs Look Like?
Just like adults, baby bed bugs usually lay on their backs when they die. Dead baby bed bugs will no longer move or try to escape, and their bodies will dry out.
If they are killed by insecticides, their bodies may curl up. And because they are very small, they will look like dark spots, which are blood traces or their feces.
What Does It Mean If I See a Baby Bed Bug?
If you see a baby bed bug, there is a very high percentage that there are a lot of them hiding somewhere.
As mentioned earlier, females lay tons of eggs, and therefore, it is very unlikely that only one of them survive. In fact, some bed bug eggs and nymphs may still be alive even after you treat a heavily infested area.
Can Baby Bed Bugs Live On Your Skin?
Baby bed bugs cannot live on human skin or any other parts of the body of their host. Like their adult version, these creepy nymphs immediately crawl away after sucking a sufficient amount of blood.
On average, both the adults and nymphs spend 3 to 10 minutes biting their victims to become engorged or fill with blood.
Are Baby Bed Bugs Harder to Kill Than Adults?
Baby bed bugs are easier to kill than adults. This is because these nymphs have softer bodies and they move slower as compared to the adult ones.
However, they are harder to find because they can hide better than their parents. They can squeeze their bodies better and look like dead bed bugs or tiny spots.
What High Temperature Can Kill Baby Bed Bugs?
According to research, adult bed bugs and nymphs will die once they are continuously exposed at 113°F (45°C) for at least 90 minutes.
Once they are exposed at 118 °F (47.77°C) for about 20 minutes only, they will also die. A 100% mortality rate is very likely to happen if you extend the time to 90 minutes.
What Low Temperature Can Kill Baby Bed Bugs?
Based on a separate study, all life stages of bed bugs could die once they are exposed to 3.2°F (-16°C) for about 3.5 days.
However, some of them may still survive if they are exposed to -13°F (-25°C) for only a short time. Meanwhile, exposure to -4°F (-20°C) for 48 hours only can result in a 100% death rate.
How Long Does It Take for Baby Bed Bugs to Die Without Feeding?
Baby bed bugs can still live up to several months without a blood meal, while older stages of nymphs can survive longer than the younger ones.
On the other hand, adults and older nymphs can still survive up to a year without feeding, under very favorable conditions. There can also be four successive adult generations a year.
Where Do Baby Bed Bugs Hide?

In general, bed bugs are neither solitary nor social creatures. Although they are mostly in groups, a single bed bug can live without any companion. But still, bed bug nymphs can also be found in places where the adults are hiding.
To give an idea, here are some very possible places where baby bed bugs usually hide:
- Buttons, seams, and zippers of your mattress
- Bed frames, box springs, headboards, and upholstery
- Inside the computers, laptops, and other electronic appliances
- Behind wall clocks, picture frames, and wall calendars
- Inside and outside corners of cabinets, storage boxes, and drawers
- Screw heads, electrical receptacles, and hinges
- Inside cracks or crevices and very tiny openings
- Old clothes and other belongings that are seldom used
- Furniture and other materials that are made of fabric, paper, or wood
How to Get Rid of Baby Bed Bugs Naturally and Effectively?
As mentioned above, baby bed bugs and their adult counterparts could be in every hidden area inside your house. Nonetheless, they are mostly hiding about 6 feet closer to beds and other resting places.
If you don’t want to use harmful insecticides, here are some natural but effective ways to get rid of baby bed bugs:
- Vacuum repeatedly all infested items and areas prone to bed bugs. Seal and dispose of vacuum bags properly.
- Wash infested bed sheets, blankets, and pillows with hot water of 122°F (50°C) for about 20 minutes.
- Place infested small items in the freezer at 0°F (-17.7°C) for 2-4 days.
- To clean infested mattresses and furniture, you can use a portable steam cleaner such as .
- Trap the bed bugs inside your mattress using an airtight encasement such as Utopia Bedding Zippered Mattress Encasement Queen .
- DE (Diatomaceous Earth) such as kills adult bed bugs and nymphs but not their eggs. This is because bed bugs will have to crawl on DE to get killed.
- Place bed bug interceptors under all bed and furniture posts. Products such as are chemical-free and very easy to use.
- If you have been traveling, don’t put your bag on the floor or bed in hotels and carefully inspect your items before packing.
- When buying second-hand couches, mattresses, or beds, inspect them thoroughly before bringing them into your home.
Related: Natural Ways to Get Rid of Bed Bugs: A Complete Guide
Summary
Baby bed bugs can be more difficult to control than adults because of their smaller size. The key here is not to assume that you have eliminated all of them in just one method. For very severe bed bug infestation, heat treatment in your house done by a professional pest control service may be necessary.
List of Sources
Sutherland, A. M., Choe, D. H., Lewis, V. R. (2013). Bed Bugs. University of California Agriculture & Natural Resources.
Miller, D. M. Using Heat to Kill Bed Bugs. Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services.
Hahn, J., Kells, S. (2021). Bed bugs. University of Minnesota Extension.
Wang, C. Methods to Control Bed Bugs. New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station.
- How to Get Rid of Copperheads | Practical Guide - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Corn Snakes | What Makes Them Aggressive? - August 27, 2023
- How to Get Rid of Alligators | Safety Measures and Removal Methods - July 16, 2023
