Cockroaches are filthy insects that can survive in extreme conditions with very limited food sources. They do not rely on humans to complete their life cycles like mosquitoes and fleas. Cockroaches rapidly outgrow in numbers and wreak havoc in your life. They are mostly active during the night and prefer to live in dark and moist corners (in drains or near leaky pipes).
Cockroaches can be a serious health risk as they can carry disease-causing viruses and bacteria. They are not aggressive in nature but are they able to bite us, humans? This is exactly what we are going to talk about in this article.
Do cockroaches bite? Cockroaches rarely bite humans. Only in some specific cases, for example, when they outgrow in numbers or when there is a lack of food, they will bite humans. There are some recorded cases of cockroaches biting fingertips, eyelashes, hands, and feet. Cockroach bites are similar to bed bug bites as they also cause red and itchy marks or bumps.
In the following sections, we have given complete information and a fact sheet about cockroaches and their bites. Additionally, we have also given you our prevention and treatment guide for their bites. Let’s begin!
Cockroach Bite| General Information
Although cockroach bites are not common, they also depend on the type of cockroach. Certain types of cockroaches will bite only when they expend all other food sources. Usually, they only feed on dead insects, meat, sweets, crumbs, fungi, etc.
The cockroach bite can be mistaken for other insect bites. For people that have sensitive skin, it can cause an allergic reaction or an itchy bump.
According to the reports of Walter Ebeling, an extract with cockroach allergens significantly affected up to 7.5% of participants among 253 normal people and the number increased by up to 28% among 114 allergic patients.
Do Cockroaches Bite Humans?
Cockroaches generally do not bite humans but whether or not they are going to bite also depends upon the type of cockroach. A study (Roth and Willis, 1960) discussed 20 reports of cockroach bites on fingertips, calloused skin, hands, or feet. However, the bites didn’t cause a serious reaction but they can lead to a small lesion, red bump, or wounded skin.
Cockroaches are nocturnal insects and they will usually bite at night time. The common spots where cockroaches tend to bite are hands, toes, fingers, face, or mouth. According to the report of Joseph G. Kunkel, the cockroach will bite at night only on one condition when you fall asleep and that is if you stay still or do not move around.

Infants and children are more vulnerable to cockroach bites than adults due to their softer skin. Cockroaches can also cause skin infections by scratching their leg spine on the skin due to their ability to carry infectious bacteria.
What Does a Cockroach Bite Look Like?
As cockroach bites look very similar to the bites of other insects, it is difficult to distinguish their bites from other insects’ bites. Their bites are confused with the bed bug bite due to similarities in shape and form. However, the cockroach bite looks slightly larger than the bed bug bite and is bright and reddish in color.
The bed bug bites appear in a group whereas cockroach bites appear once at a time. The cockroach bite can cause red bumps on the skin and its allergens can cause swelling, burning, irritation, or itching.
With people that have sensitive skin, the infected area in rare cases can also be filled with pus. The red bumps of cockroach bites are larger than mosquito bites. If you scratch the infected areas, you will worsen the area and cause rashes or more severe conditions.
Do Cockroaches Bite or Sting?
Cockroaches do not sting like wasps, bees, or other stinging insects. They bite like bed bugs or mosquitoes and leave large round red marks. However, cockroaches do not prefer human flesh and they will bite rarely.
The cockroach bite is not poisonous but it can cause a burning sensation or pain depending upon the tolerance of the infected person.
Do Hissing Cockroaches Bite?
Madagascar Hissing cockroaches do not bite like the other cockroaches. The hissing cockroach has very weak jaws that cannot bite or pinch your skin. Even if they try to bite, it won’t cause any reaction or wound. Madagascar Hissing cockroaches eat fruits, crumbs, or pet food, therefore, they do not cause any harm to humans or animals.
Do German Cockroaches Bite?
German cockroaches are the most common type of cockroach found all over the world. They prefer to eat sweets and starchy food. German cockroaches rarely bite humans and they only bite due to limited food sources or when there are too many of them.
They can bite your dead skin, hands, or toes. Their bite can cause redness, itchy skin, burning sensation, or lesion in severe conditions.
Do American Cockroach Bite?
The American cockroach is also a common pest all over the globe. They feed on dead insects, meat, and fermented food. There are reports of American cockroaches biting children’s fingernails, eyelashes, and dead skin. They can cause red bumps, wounds, or lesions on soft skin. According to studies, the American cockroach exerts a 50 times stronger bite force than its body weight.
Do Cockroaches Bite Dogs?

Cockroaches can bite cats, dogs, or other pets. The cockroach bite can itch or can cause a burning sensation (or visible scratch) in the infected area. However, cockroaches do not contain venom and they are less likely to bite dogs and other pets than humans.
Do Cockroaches Bite You in Your Sleep?
Cockroaches can be commonly seen during the night, they are mostly inactive during the day. The cockroaches will tend to bite your earlobes or fingertips when you fall asleep at night or stay still. They are usually cautious of humans and do not interact or bite when you are awake.
Can Cockroaches Bite Through Plastic?
Cockroaches can easily chew through thin plastic containers, bags, or packages to get the food. They cannot cut through thick plastic bags or containers. Make sure to keep your food inside a thick plastic container to keep it safe.
Do Cockroach Bites Itch?
The cockroach bite appears like a red mark. The red marks can also cause burning, irritation, or itchy skin. It can also lead to bumps, minor wounds, or lesions. Do not scratch the infected area because it can worsen the situation. On sensitive skin, cockroach bites can cause allergic reactions, inflammation, or other problems. The bite can also be filled with pus but this only happens in severe conditions.
It is suggested to wash or sterilize the bitten area since the cockroaches carry allergens and microorganisms. Apply ice to the infected area to lessen the swelling and burning sensation. This helps with itching as well.
How Long Do Cockroach Bites Last?
The most common types of cockroaches that can bite are American cockroaches and Australian cockroaches. The cockroach bite can last up to a week or depending upon the severity of the infected area.
The infected wound or lesion can take more time to heal. The redness or bump can be treated earlier by seeking medical care.
Are Cockroach Bites Dangerous?

Cockroaches are considered to be dangerous because they can carry disease-causing viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens in your house. They are unhygienic scavengers, that can contaminate your food or other items. However, they usually do not spread diseases through a bite.
The cockroaches transmit germs and allergens through their feces, vomit, saliva, or urine. Direct contact of cockroaches with wounds or eating contaminated food can also cause diseases.
Cockroach Bite Disease
The bites of the cockroach may not be dangerous but they can carry bacteria, allergens, or other pathogens on the body, waste, or saliva. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), cockroaches can transmit bacteria such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella to your food or utensils.
The bacteria and pathogens can further lead to dysentery, cholera, diarrhea, typhoid fever, plague, campylobacteriosis, listeriosis, intestinal diseases, and other health complications.
People that are allergic or have asthma are more susceptible to cockroach bites. The allergens they carry can trigger asthma or their bite can lead to a skin infection in patients that are susceptible to allergies. The bitten area can further cause swelling and rashes. According to recent studies, enzymes present in cockroach feces, shed parts of the body, saliva or eggs cause an allergic reaction.
Does Cockroach Bite Cause Leprosy?
Cockroaches are suspected to carry Mycobacterium leprae which is the main causal agent of leprosy. They can carry this disease through their mouth, feces, saliva, or vomit. If the infected area is not treated within time, it can cause permanent damage. The leprosy causal agent has 5 years incubation period and symptoms of the disease may appear after 20 years.
Cockroach Bite Symptoms | Side Effects
Cockroach bites can cause discomfort or pain. The reaction and pain of the bite depend upon your tolerance and body condition. The common symptoms of cockroach bites are itchy skin, reddish marks, skin rashes, sneezing, watery eyes, nasal congestion, or coughing. You may also notice the signs of anaphylaxis reactions, difficult breathing, or low blood pressure in extreme situations.
Allergic Reaction to Cockroach Bites
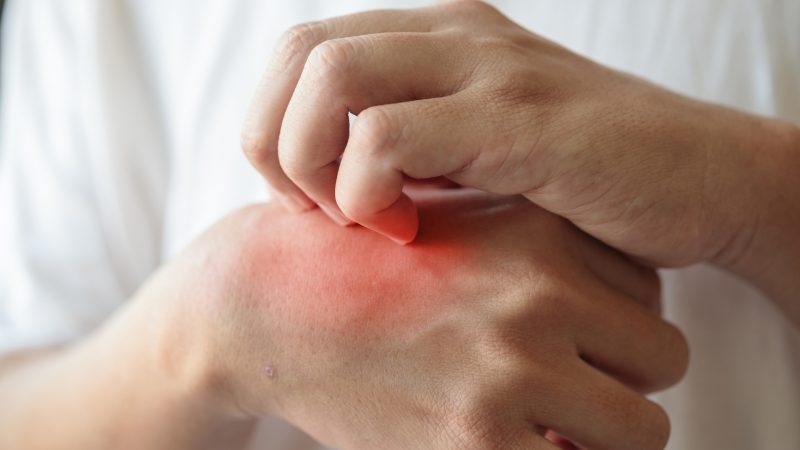
Some people can have an allergic reaction due to the specific protein present in the cockroach’s saliva. The saliva of the cockroach can transmit allergens through the bite. The allergic reaction can be severe in people with asthmatic symptoms or in infants. If anaphylaxis reactions begin to occur then immediately seek medical help.
Why Do Cockroaches Bite Eyes?
Cockroaches do not bite randomly your body. They tend to bite body parts such as the mouth, hands, toes, fingernails, or eyes. Cockroaches are attracted to the parts where food crumbs or food particles can potentially be found.
They are also drawn to the softer areas of your body such as the eyes or earlobes. Children and infants also have a soft body that’s why they are more prone to cockroach bites.
What to Do When a Cockroach Bites You?
After a cockroach bite, you should observe the symptoms and look for any allergic reaction. The infection can be minor to severe depending upon the person’s health, body part, or age. For instance, the reaction to a cockroach bite can be severe in children or in patients with allergies.
In most cases, cockroach bites do not cause any severe reaction. The infected area should be washed with warm water and soap to reduce the infection. In case of a wound, or lesion, or if you have an allergic reaction or feel other symptoms, it is suggested to take medical advice immediately.
Cockroach Bite Treatment
Cockroach bites are rare, they only bite humans when you deprive them of food. You can lessen the severe effects or infection caused by cockroach bites by correctly identifying the cockroach bite and using first aid treatment instantly. Several home remedies and medications can also help to treat the infected area.
First Aid Treatment for Cockroach Bites
When you notice a cockroach bite (redness, bump, or itching) on your body. Immediately clean the infected area to avoid the risk of infection. Start cleaning the bitten area with warm water and then wash it with soapy water.
If you are feeling itchiness, burning sensation, or swelling then use an ice pack or apply aloe vera gel. Medicated creams can also be used with the consultation of a doctor. If you have symptoms of an anaphylaxis reaction then seek medical attention instantly.
Cockroach Bite Home Remedy
Use the following home remedies to treat the cockroach bite:
Wash Infected Area
The immediate measure, you should take after a cockroach bite is the washing the infected area. Clean the bitten body part with warm water and wash it with soapy water to remove germs or pathogens from the bitten area.
Use Ice Pack
Cockroach bites can cause itching, swelling, or burning sensation. You may feel the urge to scratch the bitten part of your body. To reduce the itching and swelling, you can use ice packs. Apply ice packs until you do not feel a burning sensation any longer (for about 10 minutes). You also apply aloe vera, lemon juice, tea tree oil, or moist tea bags to reduce the itching.
Baking Soda Paste
Apply calamine lotion or antiseptic cream to reduce swelling and treat the cockroach bite. Alcohol is also used as an antiseptic to clean the infected areas and to treat inflammation. If antiseptic cream is not available, then try using baking soda and vinegar paste to soothe itchy skin.
Mix equal parts of baking soda and vinegar and apply it all over the bitten area for 20 minutes. It will disinfect the infected part and will relieve the swollen area. Rubbing an infected area with the onion slice can also help with detoxification.
Best Medicine for Cockroach Bites
Consult yourself with the doctor if you have a sensitive body or an allergic reaction. You can use antihistamine medicine (calamine lotion) with ice packs to reduce the itching or allergic reaction from the cockroach bite. Or any other anti-itching cream or hydrocortisone cream can also be applied to reduce swelling and itching.
Medication such as nasal corticosteroid spray and decongestants can be used to treat allergic symptoms. Some of the commercially available anti-itching creams for insect bites are the following:
- FAST, EFFECTIVE, LONG LASTING ITCH RELIEF: Anti-itch cream that...
- FAMILY FRIENDLY ANTI ITCH CREAM: Hypoallergenic & pediatrician...
- NATURAL & SMELLS GREAT: Organic oatmeal and menthol soothe and...
- EASY TO USE & TRAVEL FRIENDLY: Convenient stick is easy to carry,...
- SUSTAINABLE & ECO-FRIENDLY: Organic plant based ingredients +...
- ANTI ITCH GEL: Benadryl anti itch gel temporarily provides pain...
- TOPICAL ANALGESIC: Topical cooling gel contains 2% of the topical...
- SOOTHING & COOLING GEL: Carry this topical anti itch analgesic...
- POISON IVY REIEF: Topical Analgesic to provide itch relief for...
- INCLUDES: Pack of 1, 3.5 fl. oz. anti itch gel; Suitable for...
- 1-ounce tube of Benadryl Extra-Strength Anti-Itch Cream...
- Topical analgesic cream works when you need it most and provides...
- The cooling cream provides the relief of pain and itching...
- Cooling cream that provides relief from most outdoor itches...
- Intended for use by those ages 2 and up, soothing cream offers...
How to Prevent Cockroach Bites
Pest prevention is the best way to keep yourself safe from cockroach bites. Cockroaches are attracted to your house due to unhygienic conditions, warmth, humidity, or shelter. They live near leaky pipes, in dark holes or cracks.
Keep your house clean and dry to prevent them from entering your house. Repair any leaky pipes, cracks, or holes, and empty your trash bin regularly to avoid their infestation.
Cockroaches are attracted to you during the night (when you fall asleep), especially if you have food residues on your body parts. To keep yourself safe from cockroach bites, keep your body clean especially when going to sleep.
Apply cockroach traps and continuously monitor cockroach infestation to avoid getting bitten. Call professionals to eliminate cockroaches if the problem goes out of your control.
Cockroach Bite vs Bed Bug Bite
Cockroach bite looks similar to bed bug bite but they can be differentiated. A red bump appears when a cockroach or bed bug bites a person. Bed bugs bite in groups means that you will find multiple bites in one area whereas a cockroach bite shows only one round mark.
The cockroach bite mark (1-4 mm wide) is slightly larger than the one from the bed bug and mosquito bites. Bed bugs are more aggressive and bite more often than cockroaches. Bed bugs are blood-sucking insects whereas cockroaches are not bloodsuckers at all.
List of Sources
Kunkel, J. G. (2020). The Cockroach. Biology Department, College of Arts and Sciences, University of New England.
Ebeling, W. (2002). Urban Entomology, Pest On or Near Food. UC Riverside, Department of Entomology, College of Natural and Agricultural Sciences.
Sohn, M.H. and Kim, K.E., 2012. The cockroach and allergic diseases. Allergy, asthma & immunology research, 4(5), pp.264-269.
Weihmann, T., Reinhardt, L., WeiBing, K., Siebert, T. and Wipfler, B., 2015. Fast and powerful: biomechanics and bite forces of the mandibles in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. PLoS One, 10(11), p.e0141226.
- Bed Bug Surge 2025: How to Detect, Prevent, and Safely Eliminate Infestations in Top U.S. Cities - June 18, 2025
- Asian Needle Ants Invade US Homes: 2025 Guide to Identification, Risks, and Effective Control - June 11, 2025
- New World Screwworm Alert: How US Livestock Owners Can Prevent Outbreaks and Protect Herds [Summer 2025 Update] - June 8, 2025



