Snakes are incredibly flexible and known for slithering around, so you might think that snakes do not have bones, but nothing could be further from the truth. In fact, snakes have more bones than humans.
Do snakes have bones? Snakes have hundreds of bones, as they are vertebrates with skeletons. They actually have hundreds, which is more than humans do. However, unlike other vertebrates, snakes have a unique skeleton that allows them to thrive with fewer body parts.
After reading this article, you will know all about snake bones and skeletons. You will learn the structure of snake skeletons, the role of each unique snake bone, and how these bones contribute to their strength and mobility.
Snake Bone Structure
Let’s take a look at the bone structure of snakes, as it is fascinating.
What Do Snake Bones Look Like?
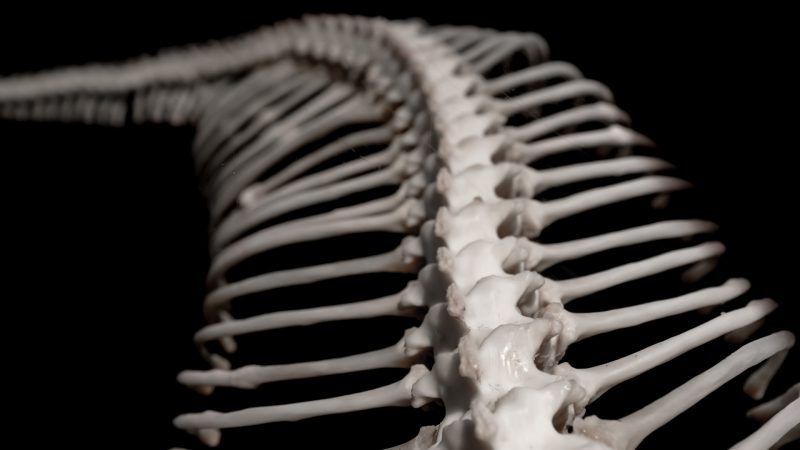
While snakes have many more bones than humans, they only have a few types of bones as compared with humans. Most of the skeleton is made up of vertebrae and ribs, making for a very basic skeleton.
The skeleton looks like a long string with rib bones attached. The bones themselves look just like bones you would see in any other animal, but snake bones are much smaller and more flexible, but they look very much the same.
Are Snake Bones Strong?
Bones are what give animal bodies their strength and structure, and despite being light and flexible, snake bones are incredibly strong. Some snakes kill their prey through constriction, meaning they use their body to squeeze their prey to death.
Even though humans have much larger bones, we are not able to do this with our prey. Therefore, snakes must have strong bones that connect with even stronger muscles to take down and squeeze animals that are many times bigger than themselves.
Are Snake Bones Poisonous?
Snakes are infamous due to the venom that some species contain in their fangs. Does this mean that the bones of a snake are poisonous too? Snake bones are not poisonous, because then many scientists would have to take great care when analyzing them.
Venomous snakes produce venom in oral glands. When snakes need venom to attack prey or protect themselves from predators, it flows into their hollow fangs. Therefore, this venom is not created nor found in any snake bones.
However, this does make the head of a venomous snake incredibly dangerous, even after death. Some people have been bitten by a venomous snake’s head hours after it died and were subsequently poisoned.
How Many Bones Does a Snake Have?
Despite being so small and having such a simple body structure, snakes have hundreds of bones in their bodies and can have anywhere from 200-400 vertebrae that make up the spine. Each vertebra is attached to a rib, meaning there are just as many rib bones as vertebrae.
The exact number of bones in a snake depends on the species. However, even the lower end of the bone count spectrum is well into the hundreds. In contrast, humans only have 206 bones.
Do All Snakes Have Bones?
All snakes are vertebrates, meaning they have an interior skeleton with a backbone, so there are no snakes without bones. Bones are the reason why snakes can slither, move around, and attack prey, so they would not be able to eat, move, or function at all without their bones.
Do Snakes Have Skeletons?
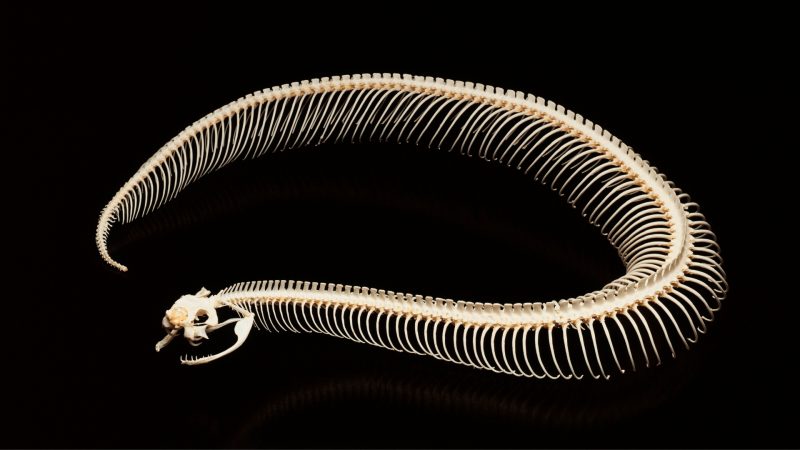
Like other vertebrates (such as humans, birds, dogs, or other animals), snakes have an internal skeleton with a backbone. But unlike other vertebrates, snake skeletons are fairly simple.
Snake skeletons are composed of a skull, a spine that spans most of the snake’s length, and a tail. The spine is connected by hundreds of interlocking vertebrae, which give the snake incredible flexibility. They also have hundreds of rib bones to protect their organs throughout their long body.
The snakehead skeleton consists of the cranium, which houses the brain, an upper jaw, and a lower jaw. Though a snake does not have ears in the same sense as humans do, the skull does contain ear bones, which are used to sense vibrations in the environment around the snake. These vibrations cause the ear bones to vibrate, which sends a signal to the brain that is interpreted as sound.
Do Snakes Have Vertebrae?
As with many animals, snake spines are composed of small interlocking bones called vertebrae. All vertebrates have vertebrae, which is why they are named vertebrates.
While humans have 33 vertebrae, snakes have anywhere from 200 to 400, depending on the species. Having so many vertebrae is why snakes are incredibly flexible and can curl up in balls, tie into knots, and twist and turn in ways that are impossible for humans. If snakes had as many vertebrae as humans, their bodies would not be nearly as flexible, and they would be completely different animals.
These vertebrae start at the snake’s skull and connect all the way to the end of his body.
Do Snakes Have Spines?
Since snakes have vertebrae, that means they have a spine, which comprises hundreds of vertebrae that take up most of the length of the snake’s body. Each vertebra of the spine is connected to a rib.
This design of the snake’s spine helps it to slither and move with an odd flexibility. If the snake’s spine were as rigid as a human’s spine, then the snake would not have been able to survive in the same way. It would probably still be a lizard-like animal with legs instead of a unique limbless animal that slithers in all sorts of ways.
Do Snakes Have Jaw Bones?
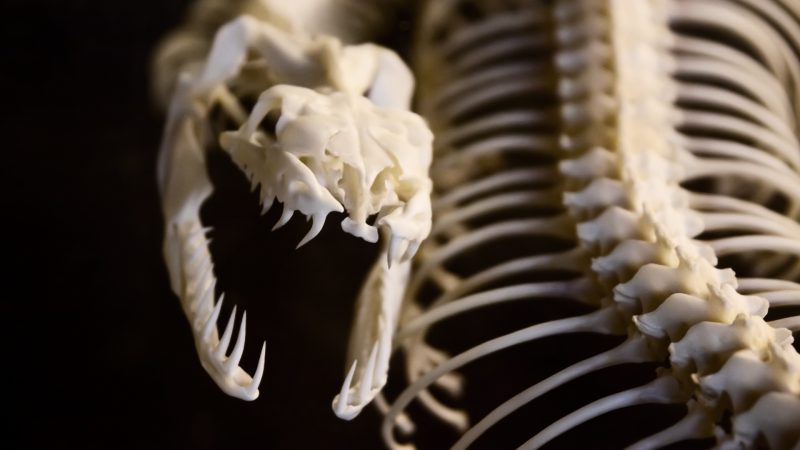
Snakes have jaw bones that are quite unique in the animal kingdom. The skulls of most animals consist of the cranium (which holds the brain), the maxilla (the upper jaw), and the mandible (the lower jaw). For most animals, the maxilla is fused to the cranium.
However, things are different for snakes. The upper and lower jaws of snakes are split into two (a left side and a right side) and are held together by flexible ligaments, which results in an extremely flexible jaw that can open up wide enough to consume prey multiple times bigger than themselves.
Do Snakes Have Leg Bones?
Snakes are unique because they do not have any appendages in their skeletons, which means that they do not have any leg or arm bones.
However, some snake skeletons have vestigial leg bones. A vestigial structure is a structure (such as a bone, tissue, or organ) that does not function, in the same way, as its ancestral form functions. Though snakes do not have full-grown legs, they have small bones that show evidence that their evolutionary ancestors had legs.
This finding has led scientists to believe that snakes descended from lizards. Though these “leg bones” do exist in snakes, that doesn’t mean that snakes will start walking anytime soon.
Snakes evolved to slither around on their bodies because it was an evolutionary advantage. The vestigial remnants of their legs only serve as a small picture of what snakes used to be, not what they will be in the future.
Related: How to Get Rid of Black Rat Snakes? | Effective, Safe, and Humane Solutions
What Makes Snake Skeletons Unique?
They are virtually entirely made of spine with a small tail, which gives them incredible flexibility but also a surprising amount of delicateness. Explore these features in greater detail to learn further about why snake bones are so distinctive.
Flexible Jaws
Snakes engage in a technique known as “gaping,” which enables them to expand their jaws wider than their bodies in order to eat food that they otherwise wouldn’t be capable of eating.
It all boils down to the jaw in this procedure. However, chewing doesn’t really matter for snakes without flat teeth. Their answer is to have a detached jaw that is only loosely joined by ligaments in the back and only connected in front by stretchy ligaments.
A human may open their jaw about 26 degrees. But a snake may stretch theirs to a full 160 degrees.
Hundreds of Vertebrae
Since snakes have a spine and vertebrae, they are classified as vertebrates. The number of vertebrae that they have distinguishes them as unique.
For the protection of our spinal cord and to hold all the nerves that enable movement, we have 33 stacked vertebrae. Snakes’ bodies range from 100 to 450 vertebrae, while their tails contain 10 to 205.
Hundreds of Ribs
A set of ribs, similar to those on a person, are located on each vertebra of a snake. 24 ribs give structure to the body and shield the vital organs within, keeping them safe. An animal with 200 vertebrae would have 400 ribs because a snake has two ribs linked to each vertebra.
The snake’s mobility is aided by these tiny, flexible ribs, which may expand and twist to a certain level. Additionally, because its ribs are sufficiently elastic to allow for extra capacity, a snake’s stomach can expand when it consumes a massive meal that is wider than its body. This is clearly seen as a sizable lump on a snake following a substantial meal.
Strong Bones
Constriction is one of the primary ways that snakes subdue their prey. When a snake constricts its prey, it coils itself around its victim and starts to gradually squeeze, tightening its hold with each exhalation of the prey. Extreme muscle and bone strength are needed for this kind of hunting, which snake has.
How To Tell If Your Snake Has Broken Bones?
Because snakes have such a unique skeleton, they do not exhibit the same symptoms humans do when they break a bone. However, there are a few signs that you can keep an eye out for.
The first sign that something is wrong with your snake is if its body has any bulges, or jagged edges, or is not its usual shape or curve. If your snake has broken one of its bones, the area may swell and look a bit jagged.
Another common sign that your snake has broken a bone is that he will become uncharacteristically aggressive if anyone goes near a specific section of his body, which is a sign that your snake is in pain and doesn’t want that area touched.
Your snake may also exhibit limited movement. If your snake moves weirdly or in a limited way, he may have a bone break or fracture.
How Do Snakes Move?

The muscles that are attached to the ribs are responsible for giving a snake its momentum. However, snakes use friction from their scales and their weight distribution to help them steer and move through their environment. So while their muscles provide the speed, their scales and weight help them with their direction.
How Fast Can a Snake Move?
Snakes move at all sorts of speeds depending on their size and species. Some snakes hardly move at all, letting their prey come to them instead. Most common snakes move around six mph, but the Sidewinder, which is the fastest snake in the world, can move at 18 mph. For context, the average human only runs about six to ten mph, although the fastest human in the world can run 28 mph.
List of Sources
Op Den Brouw, B. (2020). Sneaky Snake Facts. The University of Melbourne.
Ryan, J. (2007). Skulls and Bones: Comparing Form and Function of Vertebrate Skeletal Systems.
Knight, J. Coping With Snakes in Montana. Montana State University.
Smithsonian Channel. (2015). The Sidewinder Snake Slithers at 18 MPH.
NYU. (2009). Snakes Use Friction and Redistribution of Their Weight to Slither on Flat Terrain.
- Bed Bug Surge 2025: How to Detect, Prevent, and Safely Eliminate Infestations in Top U.S. Cities - June 18, 2025
- Asian Needle Ants Invade US Homes: 2025 Guide to Identification, Risks, and Effective Control - June 11, 2025
- New World Screwworm Alert: How US Livestock Owners Can Prevent Outbreaks and Protect Herds [Summer 2025 Update] - June 8, 2025
